Embedded Analytics: All You Need To Know


What Is Embedded analytics?
Embedded analytics, like any analytics, transforms data into charts and dashboards. The key difference is that embedded analytics, as an individual piece of software, does not look and act as a standalone solution but, instead, is integrated within another software product (app) or web portal. That integration might be purely aesthetic or fused more deeply into the underlying foundations of the two tools. Often, end users don’t even recognize that they are working with embedded analytics within their business processes and simply see it all as one tool.
As highlighted in Gartner’s definition, integrating analytics into a business process gives the end user quick and easy access to data visualizations within their daily workflow. Moreover, with seamless integration, the end user doesn’t need to switch between multiple applications (i.e., from their current workflow to a separate analytics tool).
Embedded analytics also allows software companies to obtain and fully integrate an analytics platform with their own SaaS software product without the need for heavy investment in the development of their own in-house solution.
As outlined above, embedded analytics allows companies to integrate data analytics within an end-user’s workflow (an end-user could be an internal team member or a customer). This allows the end-user to make immediate, data-driven decisions based on the insights and reports made available to them.
How Does Embedded Analytics Work?
Embedded analytics can seamlessly match the look, feel, and branding of a company’s application (the one into which it is being integrated). As previously mentioned, it becomes an integral part of the application, without anybody noticing there are actually two pieces of software turned into one.
You can either embed out-of-the box data visualization available in the analytics platform, or you can create a fully custom visualization if you need to meet specific requirements. Additionally, you can also use any third-party library and embed your desired solution.
There are several ways by which to embed data analytics, with differing levels of solution integration and flexibility. You can either embed using iframe and HTML, Web Components, or React SDK and API calls — the level of integration and flexibility of the solution depends on the embedding method employed.
Methods of Embedded Analytics
There are multiple methods by which to embed data analytics, each suitable for different use cases. As such, consider the following information when deciding on which type of embedded analytics is right for you. Each method differs in terms of both the level of data integration with the host application or web portal as well as the degree of flexibility they offer. Moreover, a different skill level is required depending on the solution in question.
The fastest and simplest method is basic embedding via iframe using an HTML snippet, while more advanced embedding techniques use React SDK and APIs. When embedding via React SDK, there are two options: using pre-built dashboards and visualizations or creating an entirely custom solution (programmatic embedding). Embedding pre-built dashboards and visualizations is a more advanced option than iframe, however, it still remains less flexible than programmatic embedding — the latter offers the most flexibility to the developer.
Web Components is another embedding method that falls between iframe and React SDK. That is to say that, it is fast to implement but offers deeper integration than iframe (but less so than SDK).
When embedding is not preferred, your data analytics can still match your branding and theming as a standalone solution with white labeling.
Below is an example of an embedded dashboard and how it can adapt to the given context.
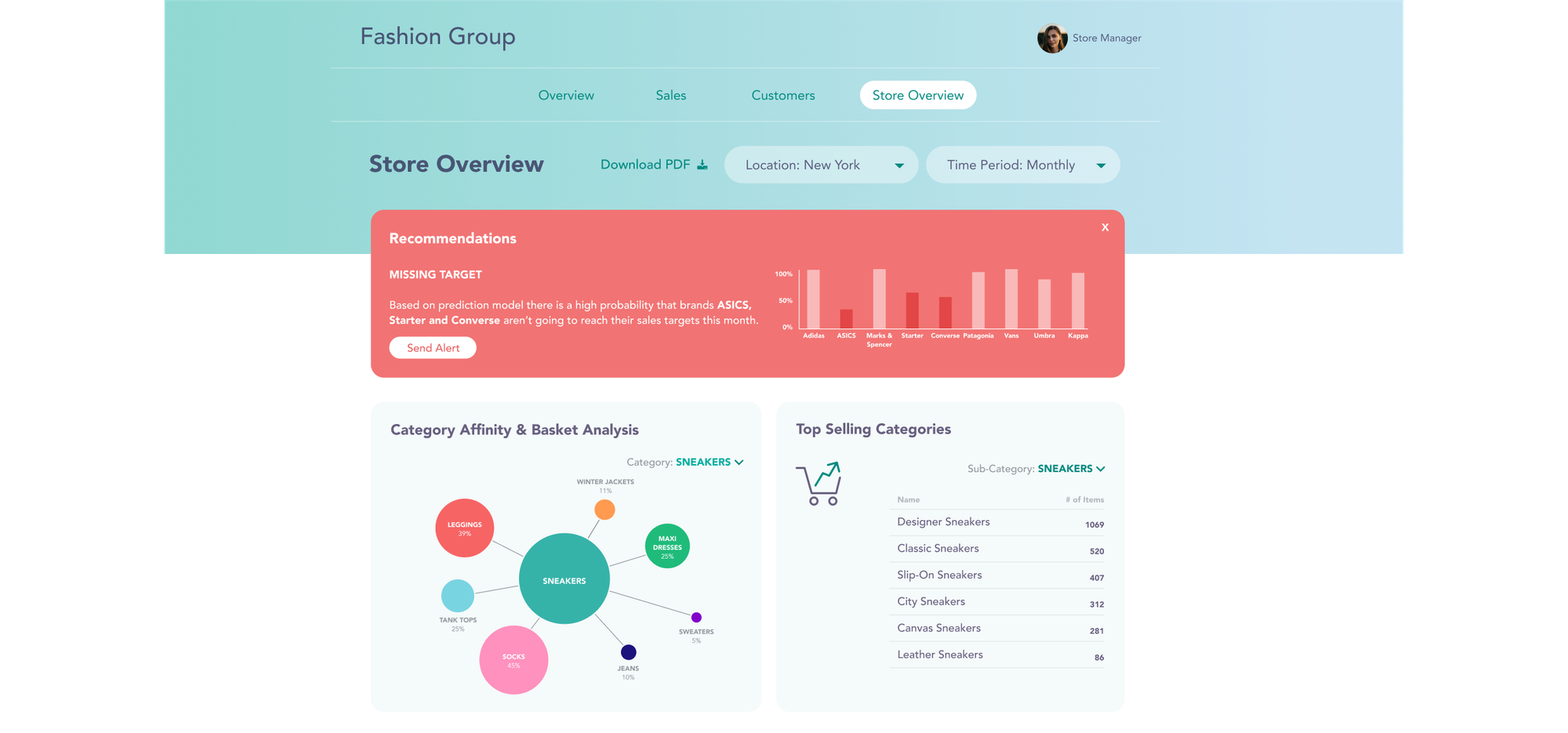
An example of an embedded dashboard
Advanced Embedded Analytics
As mentioned above, there are various methods of embedding analytics depending on the specific use case. Embedding via static iframe is just one of a number of options at your disposal. In the instance where more specialist customizations are required for the embedded solution, advanced embedded analytics known as programmatic embedding via React SDK is the right option.
Advanced embedding via React SDK enables the creation of a completely custom visualization, while the developer can code both the look and the behavior of the visualization. Advanced embedded analytics ensures deeper custom-made integration of the application and embedded visualization, great performance, and seamless interactivity.
Why Use Embedded Analytics?
There are several reasons why companies should use embedded analytics:
- Data-driven decision-making: Bringing embedded analytics to a business process gives the end-user quick and easy access to data visualizations within their daily workflow without switching between multiple applications. End users can take immediate action based on their insights and get more value from company data.
- Flexible theming: Embedded analytics, with its ability to be customized and branded, allows for adapting the analytics to the context of the application.
- Reduced time: Companies can fully integrate data analytics within their application or web portal without the need to heavily invest time and money into developing their own in-house analytics solution.
- Flexible company growth: Designed for company growth, embedded analytics allows the scalable reporting of data to thousands of separate user groups.
Key Features of an Embedded Analytics Platform
Every embedded analytics tool should provide you with the following key features:
- Engaging, self-service visualizations allow end users to create engaging, interactive visualizations via a drag-and-drop interface without the need for a data specialist.
- UI customization toolkits are an essential feature of embedded analytics, giving the ability to customize the look and feel of the visualizations and dashboards and adapt them to the whole user interface.
- AI-accelerated dashboards and visuals: Thanks to AI implemented in the embedded analytics platform, business users and analytics engineers can all work in one place. They can explore the data and interact with it, via an AI chatbot for example, automate its behavior, and adjust the code without the need to switch to any other platform.
- Automated scaling and agile change management: fully automate the separation and control of multiple user groups from different teams, locations, or companies. Platforms usually provide automated user provisioning tools, and the infrastructure secures the physical data isolation of one user/user group from another. It is impossible for users to get access to data to which they have no access rights.
- SSO(single sign-on) enables users to access embedded visualizations located within another application using only one login. It's not necessary to log in separately to see the data, as the data becomes part of one application.
- Life cycle management: ensures the alignment of any changes or new features to be rolled out to the analytics solution integrated into the SaaS product or application. When you roll out a new version or update, life cycle management allows these changes to be propagated to all clients using your product as well as the embedded analytics integrated within it.
What Is the Difference Between Embedded Analytics, Business Intelligence, and Embedded BI?
Embedded analytics and business intelligence are terms that are often used interchangeably. Both concepts take data and turn it into insights; however, the terms don't mean exactly the same thing.
Business intelligence is a process that involves people, systems, and tools collecting and preparing data for analysis to support data-driven decision-making. Embedded analytics, on the other hand, is where data analytics is tightly integrated into another application. Therefore, it provides significantly more awareness and context for decision-making.
In contrast, business intelligence can fail to deliver value, as it doesn't give the user the context that is often needed in order to make the right decision. With many BI tools, the data analytics is usually accessible within another piece of software, separate from the company's application or website. The data analytics is then often missed or underused, as end users need to log into a separate platform to access the data. On the contrary, embedded analytics is easily accessible directly within the company's software and, therefore it supports a data-focused mindset. End-users are more likely to consider data on a daily basis with the context needed to make accurate decisions.
So, what actually is embedded BI? Embedded BI is business intelligence in the form of dashboards and reports, integrated directly into the user's application. The term is often used interchangeably with embedded analytics and, as such, can be considered a synonym.
Embedded Analytics Use Cases/Who Is It For?
There are many embedded analytics use cases. As embedded analytics is designed to fit the context of the host application, it is essentially ready for any use case. In general, embedded analytics is an effective means by which to deliver data insights to customers, software companies (embedded analytics for SaaS), external partners, and internal teams. Considering its wide range of capabilities, it can be suitable for both technical and non-technical users but this is dependent on the specific solution’s capabilities. Embedded analytics is especially relevant for (but not limited to) the following industries: software companies, financial services, e-commerce, insurance, and healthcare.
Embedded Analytics Solution
What is the right embedded analytics solution suitable for every company? While different use cases will require different solutions, the right embedded analytics platform should provide:
- Self-service capabilities to support engaging, interactive data visualizations
- An intuitive UI that caters to the needs of both technical and non-technical users with, for example, API support for the former and drag-and-drop reporting for the latter.
An ideal analytics solution puts more pieces of the puzzle together - the data analytics should be embedded seamlessly, easily, transparently, cost-efficiently, securely, and without errors. Embedded analytics is an end-to-end solution for hundreds or even thousands of separated user groups and their end users with various use cases. It's important to consider long-term product profitability, where scalability and change management is crucial.
How To Embed Analytics Into Your Application?
How to actually embed analytics and who is capable of implementing it? That depends on the embedding method you choose, as well as on your technical skill capabilities. Based on your skill level you work with more or less code, which goes hand in hand with final outcome and the integration level of your solution.
As we already mentioned, there are several methods how to embed analytics, each comes with its own benefits and fits a different use case. The easiest way to embed is via iframe. That is a method suitable even for non-technical users, but it doesn't offer much flexibility. More complex way, but still without using much code, are Web Components. The last and most flexible way how to embed analytics is React SDK, which requires advanced technical knowledge. You'll find out more about embedding methods, examples, and use cases in our webinar How to embed analytics: Methods and Examples.
In most cases, you embed dashboards and visualizations pre-built in the analytics platform. Depending on the method, you use a code provided by the analytics vendor, adjust the code, and embed analytics into your application. React SDK is the only method offering an option to embed a completely custom solution, while both the look and the behavior are defined by the analytics engineer/developer. To embed analytics into your application software, you don't need to sign into the analytics platform, as all the process is done via code.
6 Requirements of Engineers for an Embedded Analytics Tool
What are the embedded BI requirements? There are a few features that every engineer should be interested in:
- What is the level of integration and flexibility of the embedding solution? The level depends on your needs and requirements.
- What are the customization options? Embedded dashboards and visuals need to be integrated into a software product so seamlessly that the end user can't tell the difference between the two pieces of software.
- What is the deployment process? Only some analytics platforms ensure quick deployment.
- Is the solution self-service? The more flexible and self-service-aligned the solution is, the more efficient the embedded analytics will be — enabling ease of access for non-technical users.
- What are the scaling options of the analytical platform? Choose a platform that enables easy scaling in terms of data volume, price, and the number of users.
- Does the embedded solution come in with any AI-fueled processes? Embedded analytics tools providing AI features can save significant time for the whole team — both when developing the solution and analyzing and drawing answers from the data.
AI and Embedded Analytics
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become an inevitable part of data analytics. It is used to enhance current analytics solutions by enabling the generation of actionable insights, forecasting, and predictive analytics along with the automation of processes.
AI has become a part of embedded BI tools, which gives embedded analytics a new dimension. Instead of just asking “what happened”, you can now ask “why it happened”. AI understands the context and provides you with the information you're looking for. Based on facts and a proper understanding of your data, you can easily predict “what will happen” in the future. With AI-accelerated embedded analytics, you can have insights providing you with a clear picture, while being directly available in your application.
Why not try our 30-day free trial?
Fully managed, API-first analytics platform. Get instant access — no installation or credit card required.
Get startedBest Embedded Analytics Tools
There are a wide variety of analytics providers on the market. Each analytics platform offers different approaches and capabilities that are usually aligned to (or more effective for) different use cases. When looking for the best-embedded analytics tools, it is essential to evaluate the platform's features including the different types of embedding offered, while considering your goals and needs. Learn the critical steps that should form a part of your evaluation journey and compare the best embedded business intelligence software.
How Much Does Embedded Analytics Cost?
The question of pricing is one of the critical criteria when evaluating data tools. There are a number of embedded analytics pricing strategies and models employed by analytics vendors, and it's important to think about which of them corresponds with the company's approach.
- Pricing per user: The platform charges per the number of active users. It is a straightforward option as money is not wasted on inactive users. This solution is ideal for internal teams, where you know how many users you need to provide access to. However, for B2B companies it is hard to estimate how many users are going to be involved, and how expensive the embedded analytics is going to be.
- Pricing per query: The company is charged for every query used to display an analytical insight or explore information in a self-service tool. Even though it may appear to be flexible, it is a highly unpredictable option.
- Pricing per workspace: The company is charged for every workspace, while one workspace can use an unlimited number of users. This option is highly predictable, as pricing can be simply calculated by counting the number of workspaces, and additional needs.
Key Questions To Ask Embedded Analytics Providers
When evaluating an embedded analytics tool there are several criteria to consider. Some of the most important questions you should ask any embedded analytics provider, in order to understand the embedding tool's key features include:
- What options do I have to embed graphs, charts, and dashboards with your analytics platform?
- Can non-technical users easily create and edit dashboards and visualizations?
- What size deployment is your analytics solution able to support? How does scaling to more users affect cost and performance?
- Which data sources are supported by your embedded analytics solution?
- What are the security standards supported by your embedded analytics platform?
Be sure to compile a list of embedded analytics key questions before choosing an analytics platform for your embedded analytics solution.
How To Monetize Your Data With Embedded Analytics?
Embedded analytics offers companies the chance to monetize their data in a number of different ways. For example, imagine that you collect data about consumer behavior related to your e-commerce website or marketplace: where they go, what they save as desired items, what they buy, and so on. All of this information can be shared with clients/retail brands via dashboards and visualizations embedded into your client portal. The data offered can be divided into tiers, with one tier provided for free (e.g., basic data insights) and the other provided for an additional fee (e.g., advanced, more detailed data insights).
As clients realize how valuable the data is, helping them to boost their operations and strategy, they will likely start requesting more detailed reports and, thus willing to pay an additional fee. By creating ‘free and paid tiers within your data offering as described, you can tap into a new revenue stream and gain measurable ROI on your embedded analytics investment.
Ready To Get Started?
Are you planning on embedding analytics into an app or portal? To see first-hand what GoodData's embedded analytics platform can do, start a free trial or request a demo today.
Want To Know More About Embedded Analytics?
To learn more about embedding data analytics and BI, continue reading via the links below.
DashboardView: Advanced Embedded Analytics
Embedded Analytics: An Alternative to Power BI
Best Practices for Building a Data Product With Embedded Analytics
The Future of Embedded Analytics
Starter Guide: Embedded Analytics in Your Software Product
Tech Guide: Your Go-to Guide to Launching Branded & Embedded Analytics
Headless BI + Embedded Analytics: Differences and Purposes
Understanding the ROI of Embedded Analytics
Why not try our 30-day free trial?
Fully managed, embedded analytics platform. Get instant access — no installation or credit card required.
Get started

