What Is Cloud Native in Analytics?


Cloud native is today’s cloud computing. It focuses on building and deploying applications, delivered to end users via the cloud model. Additionally, it provides benefits such as scalability, flexibility, and resilience.
Being cloud-native reduces the costs and considerable investments that traditional infrastructure requires, and it encompasses the deployment of microservices packaged into containers. (To learn the basics of cloud native, read our blog post What Is Cloud Native?; it also explains cloud-native architecture.)
What Is Cloud-Native Analytics, and How Can It Be Deployed?
To put it simply, cloud-native analytics seeks to provide essentially the same outcome as traditional analytics: the analysis of data to generate reliable reports that advise future business-critical decisions.
However, while traditional analytics takes the form of one, rigid platform — often only presenting the facts of the current situation — cloud-native analytics takes full advantage of cloud computing. It runs in a container-based architecture and subsequently reduces ordinary hardware costs and managerial responsibilities. Ultimately, it helps companies more effectively scale their business.
Deploying cloud-native analytics can be done through different types of clouds. Here are the main three types:
- Public cloud: This shares cloud services among customers, whereby data and applications are securely separated from other users.
- Private cloud: As the name suggests, a private cloud is specific to a given customer. It delivers a higher level of security and privacy via firewalls, preventing third parties from accessing sensitive data.
- Hybrid cloud: A hybrid cloud refers to a computing environment that combines private and public clouds, allowing for the sharing of data and application between them.
Image credit: thymos.engineering
How Does Cloud Analytics Work?
Cloud analytics is based on a software system hosted via the internet, with the system running on servers in a remote data center. The process of obtaining data for complex reports takes place in three basic steps:
- Data management: Users collect data about the performance of their business. This data has an assigned type and structure stored in data warehouses directly connected to the cloud, accessible from anywhere.
- Data analytics: A number of back-end processes prepare various composable views on related data at a large scale. They make future predictions faster and more effectively based on real-time analytics and predefined measures.
- Analytics distribution: To store and distribute data and results via the cloud, companies scale quickly and easily. The analytical tool supports data visualization through insights.
Experience GoodData in Action
Discover how our platform brings data, analytics, and AI together — through interactive product walkthroughs.
Explore product toursThe Differences Between Cloud-Native Analytics and Analytics
In comparison to its traditional counterpart, cloud-native analytics requires far less work to set up and maintain. This is due to the fact that the cloud provider is responsible for much of the infrastructure-related heavy lifting.
Another plus for cloud native is that of the standardized methods and interface employed, resulting in development that is considerably more accessible to end users. On top of these benefits, cloud-native analytics is able to fully replace traditional analytics with the added benefits that cloud computing naturally provides.
| Traditional Analytics | Cloud-Native Analytics |
|---|---|
| Requires a fully operated architecture | Runs on servers managed by cloud providers |
| Typically located on computers | Accessible anytime from anywhere |
| Frequent troubleshooting outages | Updates or bug fixes can be deployed without limitation of end users |
| Parts of analytics are composed all in one piece | Services run in separated microservices packed in containers |
| Continuous deployment is difficult and managed manually | Easy deployment through existing processes such as CICD pipelines, etc. |
| Difficult to scale due to different modules that have competing resource requirements | Easily scalable in terms of storages and resources, depending on various company requirements |
| Relies on caching and copying data | Built for real-time analysis |
| It helps to decide according to a hypothesis | Analysis based on objective views to make an impartial decision |
Cloud-Native Analytical Platform With GoodData
GoodData offers customers a cloud-native analytical platform: GoodData.CN. GoodData's cloud-native platform uses Docker containers and microservices running on Kubernetes clusters to dynamically expand analytics on demand.
In order to provide application developers with as many compute and storage resources as they can afford, whether in a public cloud or on-premises IT environment, GoodData.CN uses Kubernetes' orchestration capabilities. To be more specific, the solution works with a Helm chart for different cloud providers — or, in other words, a group of files that explain a set of connected Kubernetes resources. Additionally, customers can install GoodData.CN to different cloud storage solutions such as Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure Cloud.
One of the major benefits of GoodData.CN is its ability to provide a programmatically managed and controlled headless analytics solution. Users can connect to the analytics engine, build a semantic data layer on the top of a data source’s — or combined data source’s — physical data model, and then create custom metrics. GoodData supports creating metrics via its own multi-dimensional query language, MAQL. (For more information on MAQL, check out the GoodData University course.) Afterward, custom analytics insights and dashboards can be built on top of the MAQL-based metrics and embedded into an application or web portal, or utilized in the desired analytics use case.
Moreover, GoodData's headless BI engine supports the consumption and visualization of data from any third-party application, with self-service analytical tools empowering technical and non-technical users to customize their own data visualizations. This customization function can be facilitated through all the standard channels, such as protocols (JDBC, ODBC), SDKs, or open APIs. (To find out more information about GoodData.CN, read this Medium post on headless BI.)
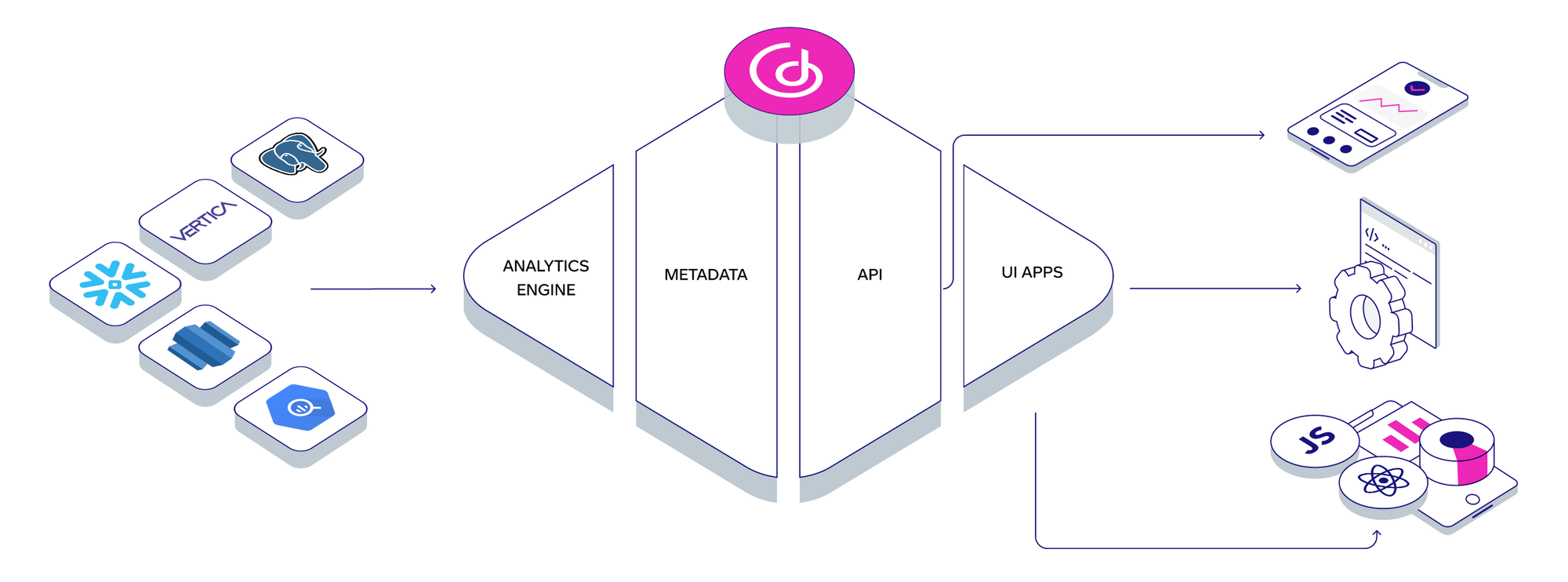
GoodData.CN provides many benefits, including the ability to:
- Run simultaneously without limiting end users
- Provide a deployable analytical engine anywhere
- Be deployed in a public or private cloud
- Store and manage workspaces as individual objects
- Provide real-time analytics directly connected to a user's data sources
Ready to Learn More?
If you are interested in GoodData.CN, please contact us. Alternatively, sign up for a trial version of GoodData Cloud: https://www.gooddata.com/trial/
Experience GoodData in Action
Discover how our platform brings data, analytics, and AI together — through interactive product walkthroughs.
Explore product tours

