AI Memory
Experimental Feature
This is an experimental feature. It is in active development and may be significantly changed or removed.
AI Memory gives you a way to fine-tune how the GoodData AI Assistant understands and answers business questions. It lets you define additional workspace knowledge that guides the Assistant’s tone, terminology, and logic so users always get accurate and consistent responses.
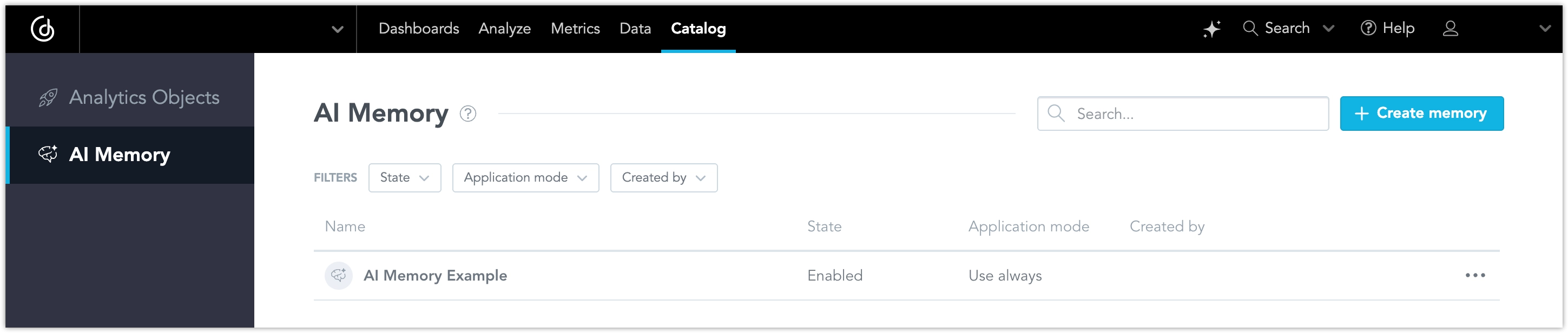
Organization Admins or Workspace Admins with the AI_ASSISTANT permission can access this feature from Catalog → AI Memory.
Example:
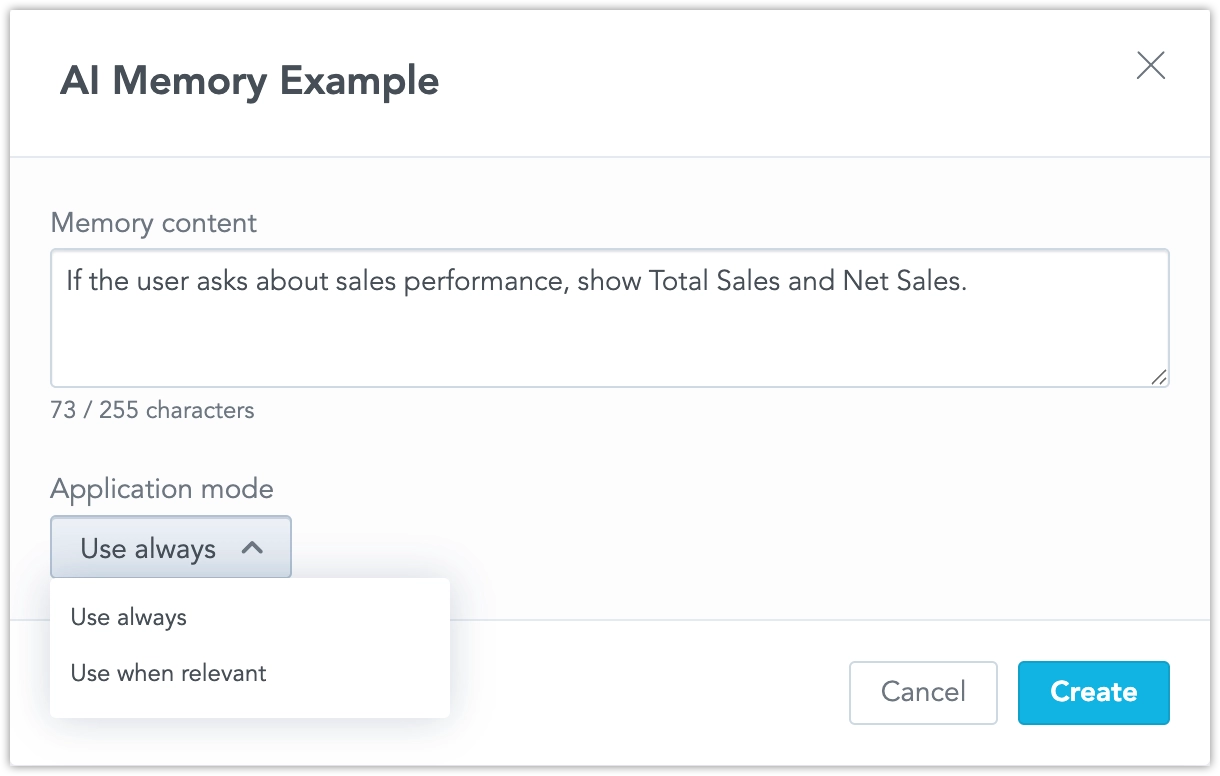
If users often ask for “sales performance,” but your semantic model does not include a metric with that exact name, you can create an instruction that tells the AI to use Total Sales and Net Sales together whenever someone asks about “sales performance.”
This ensures consistent, predictable behavior without modifying the underlying data model.
Note
AI Memory supplements your semantic layer but does not override its logic or permissions. It adds guidance and interpretation, not new data definitions.
How AI Memory Works
You can use AI Memory to give the AI Assistant Instructions. These are rule-based mappings that define how the AI should respond to specific types of questions. These can be simple mappings or conditional rules that apply only when relevant.
Examples
- If the user asks about sales performance, show
Total SalesandNet Sales. - If the user asks about regional performance, filter by
EuropeandNorth America. - Use a professional tone in all responses.
Instructions can control both content (what information is returned) and style (how responses are written).
Each instruction includes:
- Short name: A clear identifier for easy management.
- Memory content: The text of the rule or behavior.
- Application mode: Choose whether the rule applies “always” or “when relevant.”
Note
You can temporarily disable an instruction to test changes or adjust how the Assistant responds to queries.
Current Limitations
- AI Memory entries are static and must be updated manually.
- Too many overlapping entries may reduce AI flexibility.
- Entries apply globally within a workspace and may cause conflicts in multi-team environments.
- Fallback visualization settings are not stored.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Who can define AI Memory entries?
A: Organization Admins or Workspace Admins with the AI_ASSISTANT permission.
Q: How is AI Memory different from data modeling? A: Data modeling defines structure, while AI Memory defines interpretation and expected behavior.
Q: Will AI Memory override semantic layer rules? A: No. It supplements the semantic layer but cannot override logic or permissions.