Create a MySQL Data Source
Follow these steps to connect to MySQL and create a MySQL data source:
Refer to Additional Information for additional performance tips and information about MySQL feature support.
Configure User Access Rights
We recommend creating a dedicated user and user role specifically for integrating with GoodData.
Steps:
Create a user role and grant it access rights:
CREATE ROLE {role_name}; GRANT SELECT ON {database_name}.* TO {role_name};Create a user and assign them the user role:
CREATE USER {user_name}; GRANT {role_name} TO {user_name};Make the user role default for the user:
ALTER USER {user_name} DEFAULT ROLE {role_name};
Create a MySQL Data Source
Once you have configured your MySQL user’s access rights, you can proceed to create a MySQL data source that you can then connect to.
Steps:
On the home page switch to Data sources.
Click Connect data.
Select MySQL.
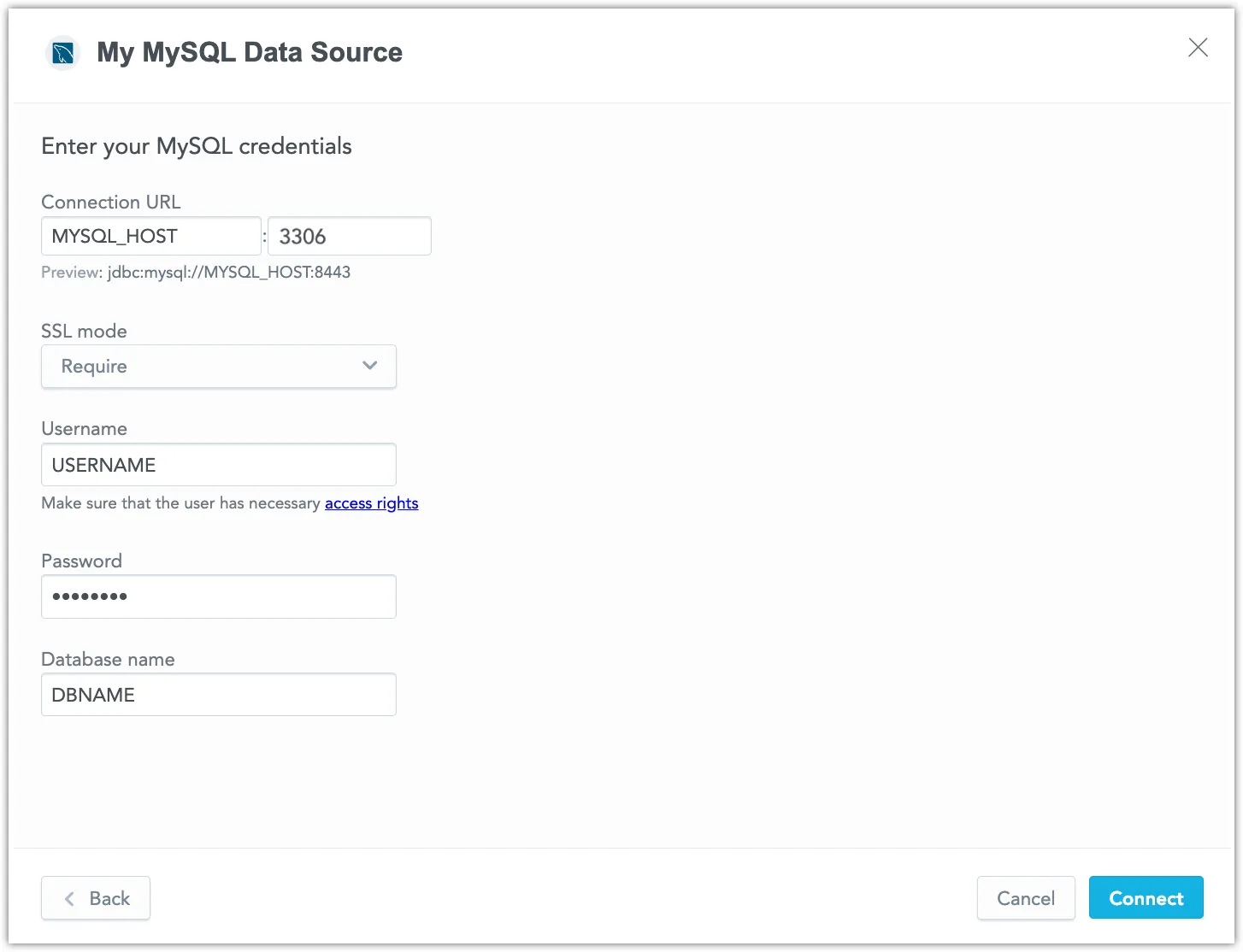
Name your data source and fill in your MySQL credentials and click Connect:
Click Save.
Your data source is created!
Steps:
Create a MySQL data source with the following API call:
curl $HOST_URL/api/v1/entities/dataSources \ -H "Content-Type: application/vnd.gooddata.api+json" \ -H "Accept: application/vnd.gooddata.api+json" \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $API_TOKEN" \ -X POST \ -d '{ "data": { "type": "dataSource", "id": "<unique_id_for_the_data_source>", "attributes": { "name": "<data_source_display_name>", "url": "jdbc:mysql:https://<MYSQL_HOST>:3306/<MYSQL_DBNAME>", "schema": "<MYSQL_DBNAME>", "type": "MYSQL", "username": "<MYSQL_USER>", "password": "<MYSQL_PASSWORD>" }}}' | jq .To confirm that the data source has been created, ensure the server returns the following response:
{ "data": { "type": "dataSource", "id": "<unique_id_for_the_data_source>", "attributes": { "name": "<data_source_display_name>", "url": "jdbc:mysql:https://<MYSQL_HOST>:3306/<MYSQL_DBNAME>", "schema": "<MYSQL_DBNAME>", "type": "MYSQL", "username": "<MYSQL_USER>" } }, "links": { "self": "$HOST_URL/api/v1/entities/dataSources/<unique_id_for_the_data_source>" } }
Additional Information
Ensure you understand the following limitations and recommended practice.
Data Source Details
Supported Versions:
- Version 5: Not supported, as it has reached end of support.
- Versions 6 and 7: Do not exist.
- Version 8+: Supported and tested.
A typical JDBC URL may look like this:
jdbc:mysql:https://<host>:<port>/<databaseName>For secured connection using SSL include
?sslMode=required.Note that we append the
permitMysqlScheme=trueparameter to all MySQL JDBC URL calls.Basic authentication is supported. Specify
userandpassword.GoodData uses up-to-date drivers.
Unsupported Features and Limitations
GoodData does not currently support the following features:
- The following functions are not supported:
- MEDIAN
- PERCENTILE
- CORREL
- COVAR
- RSQ
- SLOPE
- INTERCEPT
- Filtering by boolean columns is not supported
- There are known issues when using SQL datasets with a MySQL database:
- Converting a regular dataset into a SQL dataset generates an invalid query. You have to manually rewrite it to make it work.
- SQL datasets are not supported if the query contains one of these data types: TINYINT, FLOAT, DECIMAL, DOUBLE UNSIGNED.
- When converting to SQL dataset, the MySQL YEAR data type is converted to STRING.
- We do not currently support multiple hosts for MySQL JDBC URLs.