Create a MongoDB Data Source
Follow these steps to connect to MongoDB and create a MongoDB data source:
Refer to Additional Information for additional performance tips and information about MongoDB feature support.
Configure User Access Rights
We recommend creating a dedicated user and user role specifically for integrating with GoodData.
Steps:
Connect to your MongoDB instance and create a user with read permissions for the target database:
use <database_name> db.createUser({ user: "<user_name>", pwd: "<password>", roles: [{ role: "read", db: "<database_name>" }] })Verify that the user can access the database and collections:
mongo "mongodb+srv://<user_name>@<MONGODB_HOST>/<database_name>" --password "<password>" show collections
Configure the MongoDB BI Connector
GoodData connects to MongoDB through the MongoDB BI Connector, not directly to MongoDB.
The BI Connector exposes MongoDB data as a SQL interface, which GoodData uses for querying and analytics.
You must install, configure, and deploy the MongoDB BI Connector before creating your data source in GoodData.
Steps:
Install and enable the MongoDB BI Connector, see the MongoDB BI Connector installation guide.
Prepare a configuration file for the BI Connector that defines the connection to your MongoDB instance.
Example configuration yaml file:
## This is a example configuration file for mongosqld. ## The full documentation is available at: ## https://docs.mongodb.com/bi-connector/master/reference/mongosqld/#configuration-file ## Network options - configure how mongosqld should accept connections. ## https://docs.mongodb.com/bi-connector/master/reference/mongosqld/#network-options net: bindIp: "0.0.0.0" # To bind to multiple IP addresses, enter a list of comma separated values. port: 3307 ssl: mode: "disabled" systemLog: ## The path to the file where log output will be written to. ## Defaults to stderr. # path: <string> # quiet: false ## 0|1|2 - Verbosity of the log output, this is overridden if `quiet` is true. verbosity: 2Ensure it’s reachable from your GoodData instance and that the correct port (default
3307) is open.You can test your setup by connecting to the BI Connector endpoint with a MySQL client:
mysql -u <user_name> -p --host <BI_CONNECTOR_HOST> --port 3307 --ssl-mode=REQUIRED
Create a MongoDB Data Source
Once your MongoDB user is configured, you can create a MongoDB data source and connect it to GoodData.
Steps:
On the home page, switch to Data sources.
Click Connect data.
Select MongoDB.
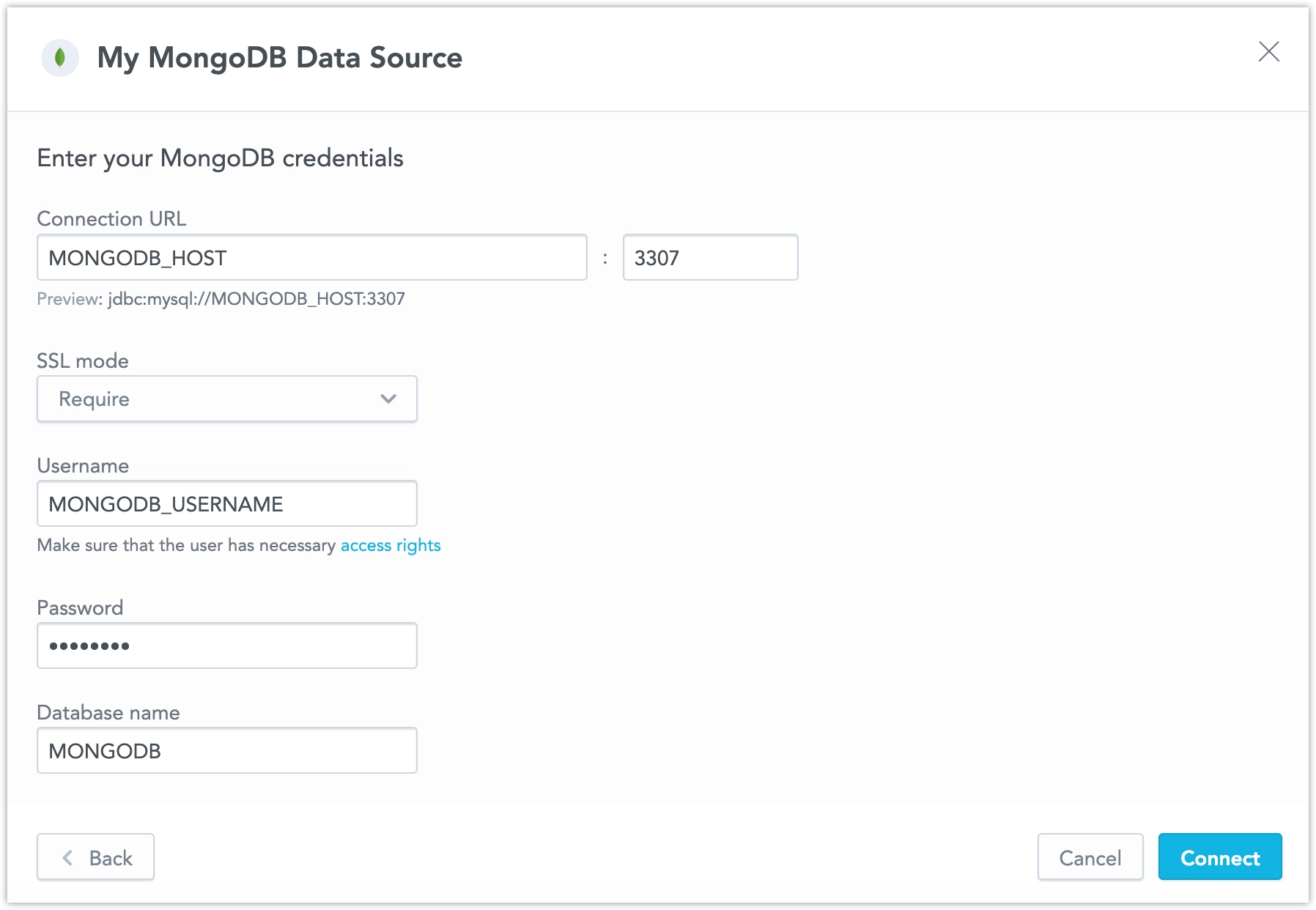
Name your data source and fill in your MongoDB credentials and click Connect:
Click Save.
Your data source is created!
Steps:
Create a MongoDB data source with the following API call:
curl $HOST_URL/api/v1/entities/dataSources \ -H "Content-Type: application/vnd.gooddata.api+json" \ -H "Accept: application/vnd.gooddata.api+json" \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $API_TOKEN" \ -X POST \ -d '{ "data": { "type": "dataSource", "id": "<unique_id_for_the_data_source>", "attributes": { "name": "<data_source_display_name>", "url": "mongodb+srv://<MONGODB_HOST>/<MONGODB_DBNAME>", "schema": "<MONGODB_DBNAME>", "type": "MONGODB", "username": "<MONGODB_USER>", "password": "<MONGODB_PASSWORD>" } } }' | jq .To confirm that the data source has been created, ensure the server returns the following response:
{ "data": { "type": "dataSource", "id": "<unique_id_for_the_data_source>", "attributes": { "name": "<data_source_display_name>", "url": "mongodb+srv://<MONGODB_HOST>/<MONGODB_DBNAME>", "schema": "<MONGODB_DBNAME>", "type": "MONGODB", "username": "<MONGODB_USER>" } }, "links": { "self": "$HOST_URL/api/v1/entities/dataSources/<unique_id_for_the_data_source>" } }
Additional Information
Ensure you understand the following limitations and recommended practice.
Data Source Details
Typical JDBC URL may look like this:
jdbc:mongodb:https://<host>:<port>/<databaseName>For secured connection using SSL include
?sslMode=verify-full.Basic authentication is supported. Specify
userandpassword.GoodData uses up-to-date drivers.
Performance and Modeling Recommendations
MongoDB is primarily designed for transactional workloads, not analytical workloads.
The MongoDB BI Connector makes it possible to use MongoDB with GoodData, but performance depends on how the data is modeled and prepared.
Recommendations:
Use pre-aggregated and denormalized data.
JOIN operations between collections (for example, using$lookup) are slow and should be avoided.
Where possible, store related attributes together in the same document.Keep data in a single collection.
For analytical use cases, structure data so that most queries can be executed against one collection rather than across multiple collections.Flatten nested structures.
Arrays and deeply nested documents should be simplified or flattened before analysis.
Note
The MongoDB BI Connector enables analytics connectivity but is not optimized for large-scale analytical workloads. For complex reporting or heavy aggregations, consider exporting data to an analytical database such as Snowflake, BigQuery, or PostgreSQL.
Unsupported Features and Limitations
Most current limitations are due to the limited feature set of the MongoDB BI Connector, which GoodData uses to query MongoDB data.
Unsupported Operations
- Statistical and regression functions such as
VAR,STDEV,RSQ, and similar. - Window functions - all ranking and running total function (for example
RUNSUM,ROW_NUMBER,RANK,TOP,BOTTOM) are not supported. - Aggregation or analytic queries using unsupported SQL syntax may return incomplete or null results.
Date and Time Handling
- The MongoDB BI Connector is stricter than MySQL when processing dates, especially with the
STR_TO_DATEfunction.- Example:returns
STR_TO_DATE('2025-09-07 12:4:60', '%Y-%m-%d %H:%i:%s')NULLdue to the missing leading zero in the minutes position.
- Example:
- The connector does not raise warnings or errors when date parsing fails, queries may silently return incorrect results.
- Week-based date formats (for example,
%v,%w) are not supported, which may affect filtering or grouping by weeks. - In GoodData.CN, MAQL-to-SQL conversion uses less strict date formats (
%Y-%c-%einstead of%Y-%m-%d), so filtering or grouping by date should behave similarly to MySQL. - Time zones are not supported. The
TIMESTAMP_TZcolumn type and time zone–aware timestamps are currently unavailable.
Other Limitations
- Boolean filtering may behave inconsistently depending on how values are stored.
- Complex nested structures and arrays may need to be flattened before use.
$lookupoperations and cross-collection joins are not supported.- Some MongoDB-specific data types (for example,
ObjectId,Binary,Datearrays) may not be fully compatible.