Use AI Assistant
The AI assistant adds a conversational layer to GoodData, letting you ask questions in plain language and get answers that align with the metrics, datasets, and business terms already defined in your semantic model - no knowledge of SQL or MAQL is required.
The assistant can also search existing dashboards, visualizations, and metrics, create new visuals on the fly, refine its output based on follow‑up instructions, and even field general questions about your data.
Every query is interpreted through the semantic layer and sent to the language model as metadata only, so raw data never leaves your environment. Responses are fully traceable since the exact metrics and filters used in the answer are always listed.
For developers, we also support working with the assistant via our API, as well as our React and Python SDKs. You can start by reading our the introductory article on our blog, or head straight to GoodData.UI, Python SDK or API documentation.
The assistant is currently optimized to work with the English and Brazilian Portugese languages. Support for other languages is planned for future releases.
This feature is still in active development and we are aware of certain limitations.
Access AI Assistant
Before you can chat, an administrator must first configure the assistant. Once configured, the assistant is available in any workspace where you have the AI assistant user permission.
Open a workspace and click the assistant icon in the upper‑right corner.
A chat panel slides in on the right.
Hit the expand icon to stretch the panel for longer conversations.
Ask Business Questions
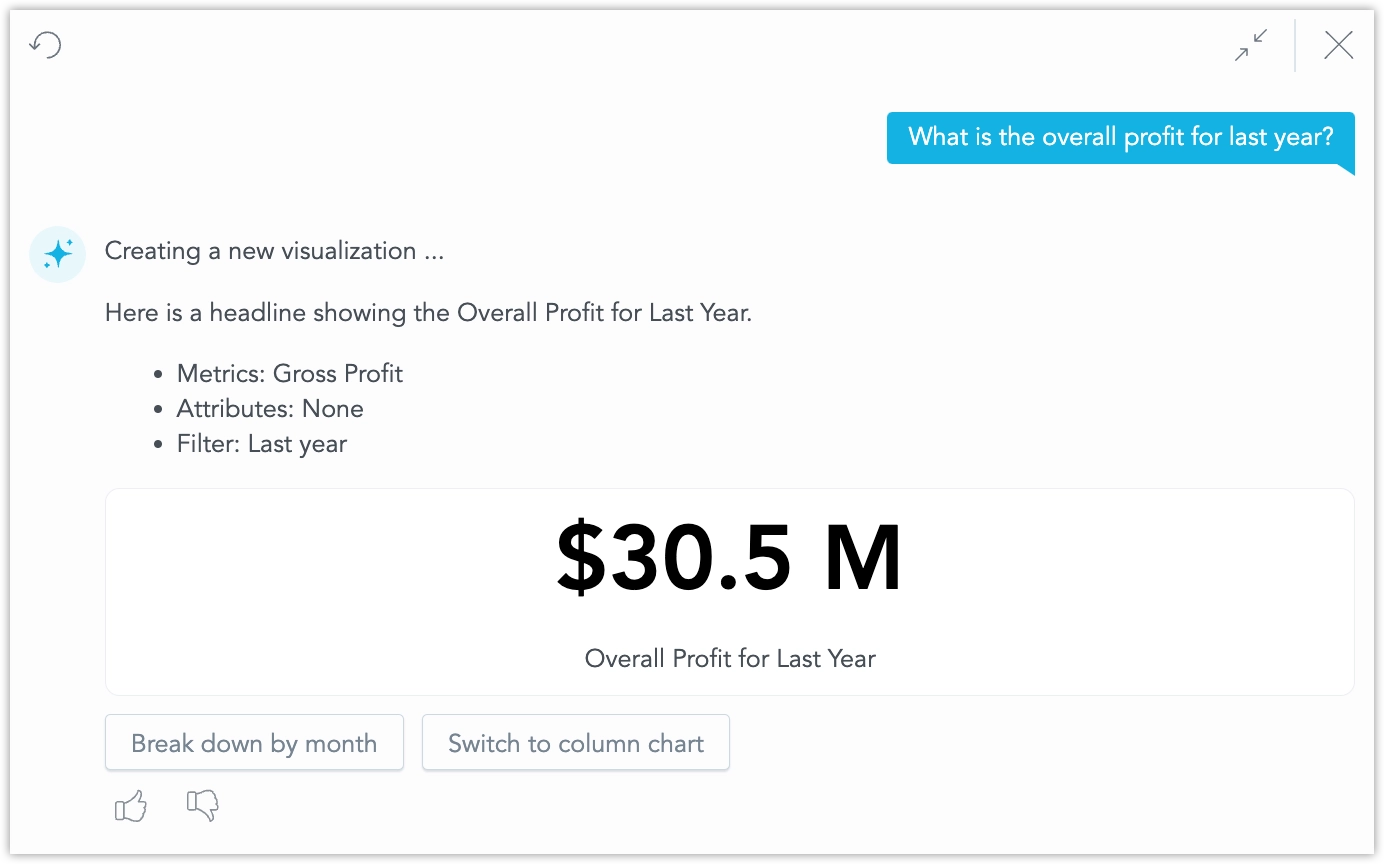
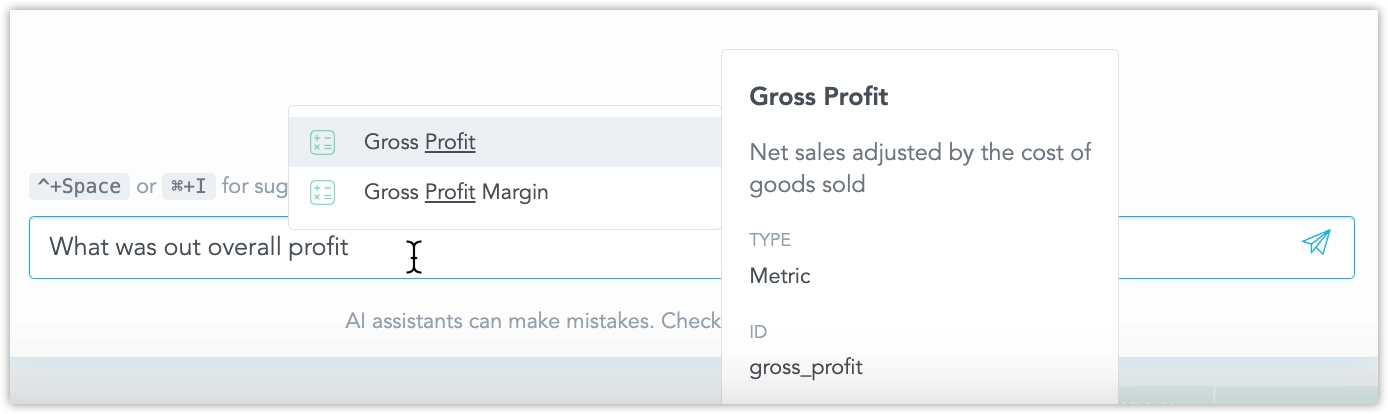
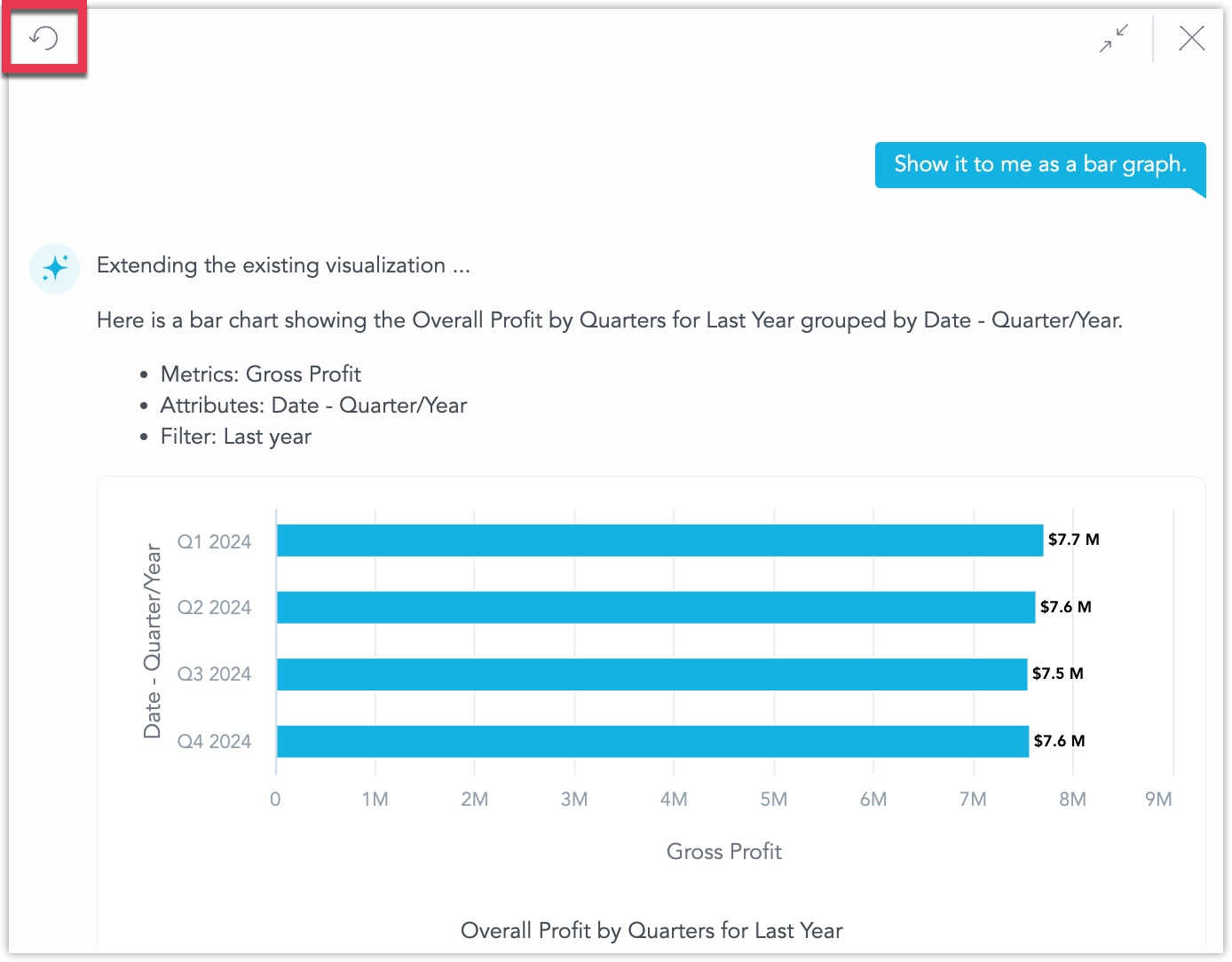
Type a plain language question such as “What was our total profit last year?”. The assistant translates the request into a metric query and returns the answer as a visualization - in this case, a headline:
While you type, the Assistant offers autocomplete suggestions drawn from existing metrics, attributes, and facts. This helps you confirm field names and, when several similar objects exist, choose exactly the one you need:
TIP
The clearer you make your metric names and descriptions, the better the assistant’s answers will be.
However, if multiple metrics, dimensions, or filters match a user’s question, the AI Assistant asks clarification questions to help users choose the correct object. This is an experimental feature that ensures accurate results even when similar or overlapping data objects exist.
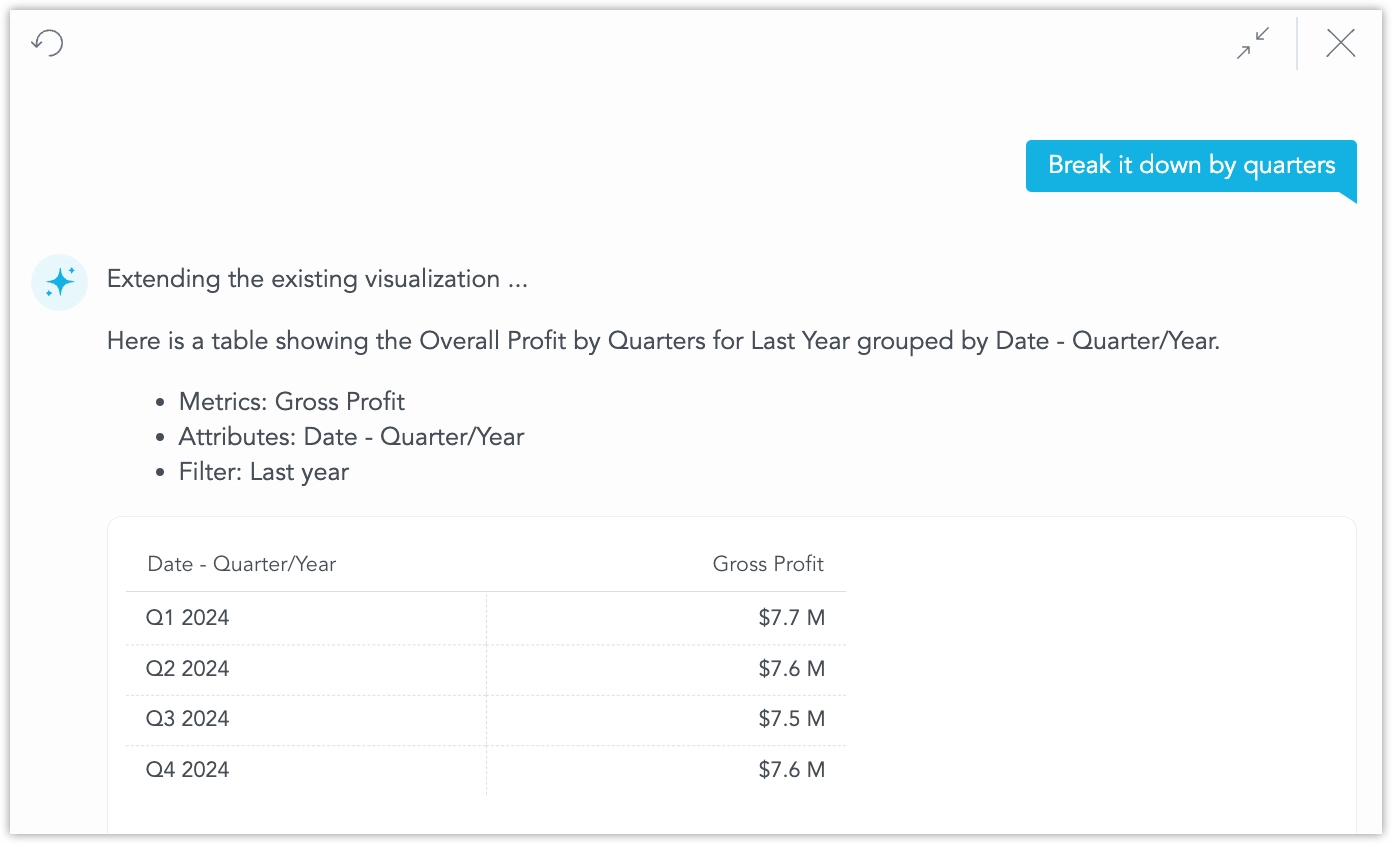
Follow‑up questions stay in context. For example, “Break it down by quarters” produces a table with one row per quarter:
The assistant tries to select a type of visualization that best fits your query.
Save Visualizations
The assistant can create the following types of visualizations:
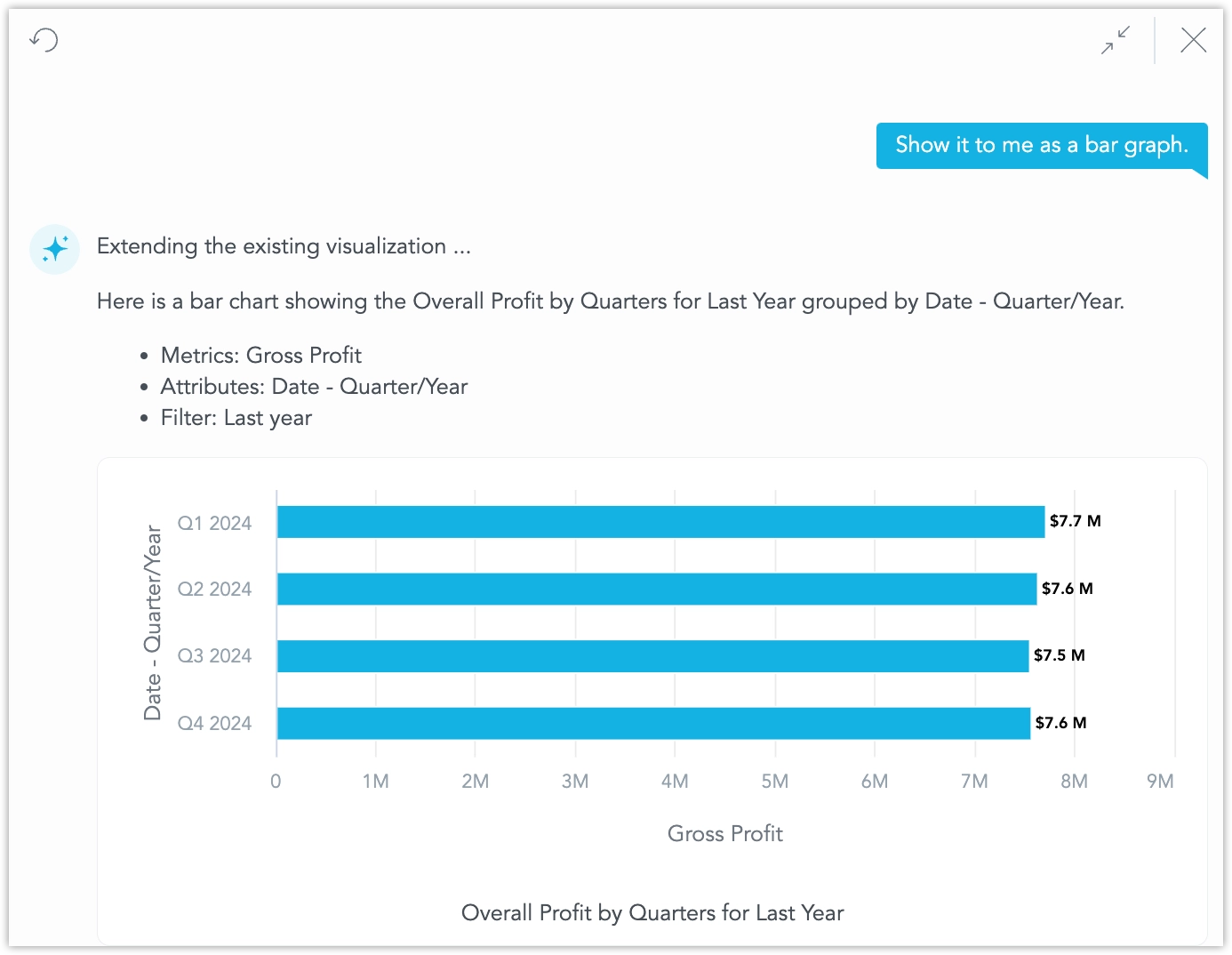
You may specify the type directly, for example by asking it to “Show it as a bar chart.”
For attributes, the generated visualizations use default labels.
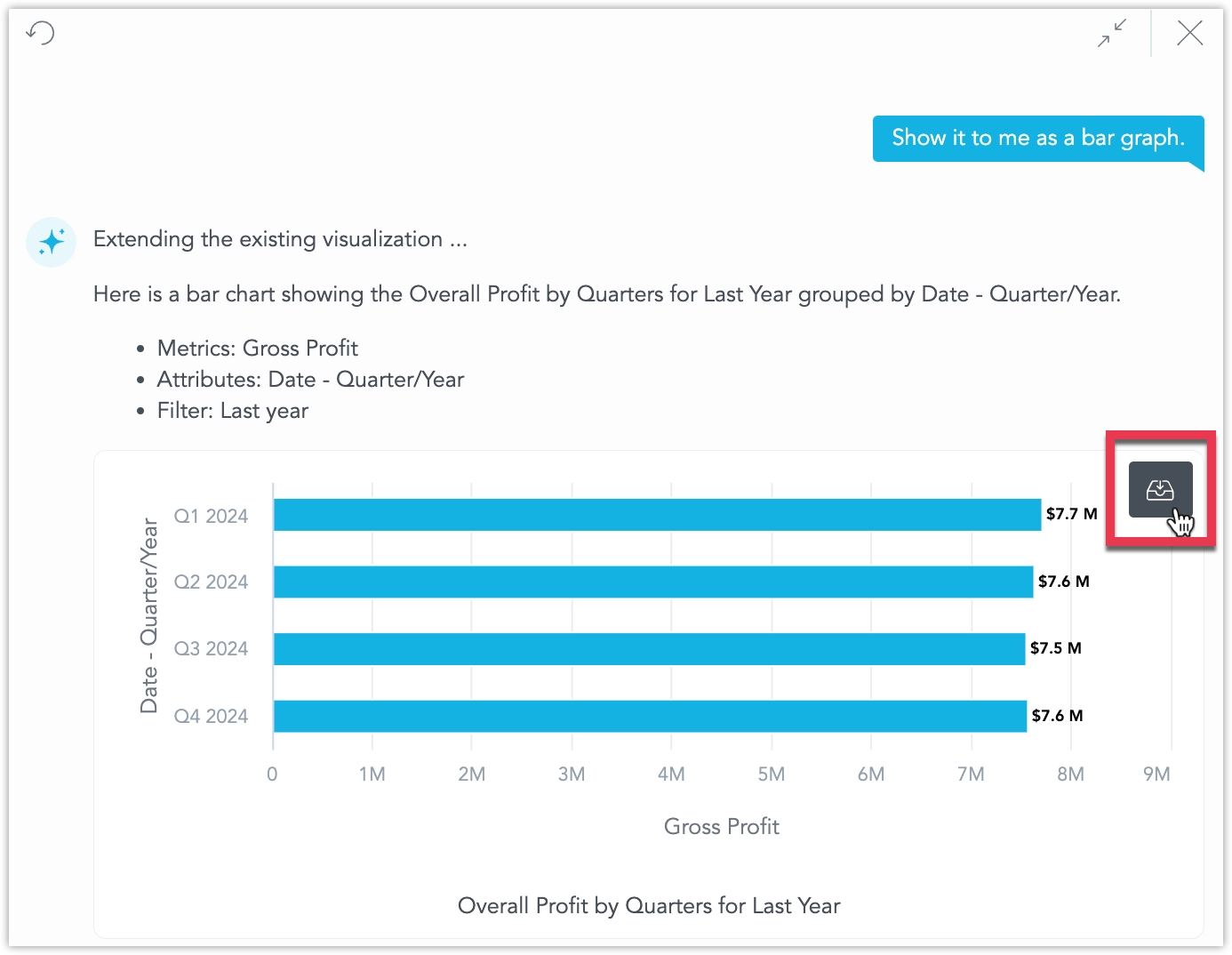
Hover over the visualization and click the save icon in its upper‑right corner.
After naming it, the chart is saved to the workspace and is ready for tweaks in Analytical Designer or immediate placement on a dashboard.
Need a fresh start? Click the reset icon in the upper‑left corner of the chat to clear the conversation.
Unless reset, the assistant remembers your conversation in each workspace separately.
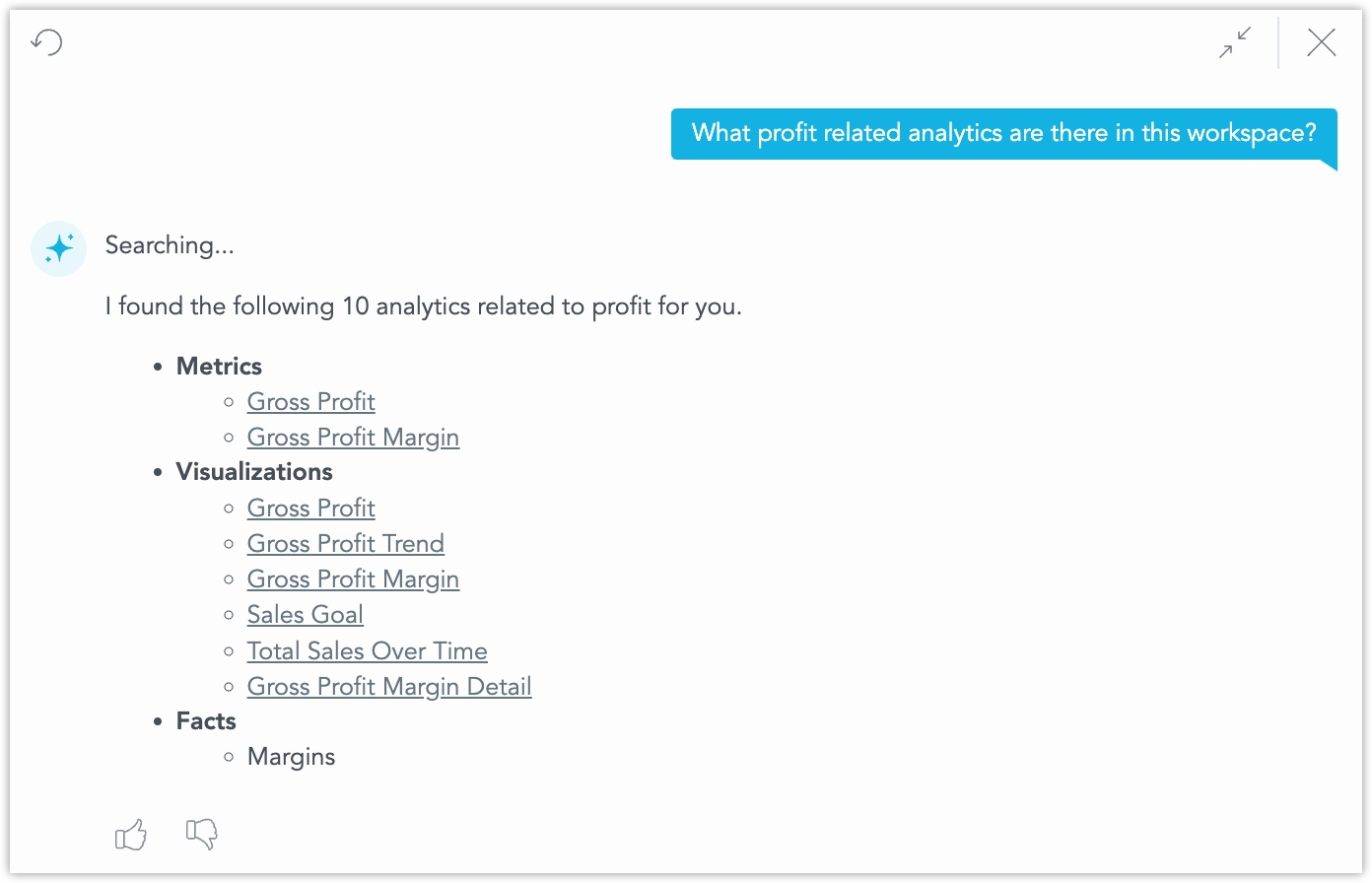
Search Workspace
You can use the assistant to search the workspace for:
- Dashboards
- Visualizations
- Metrics
- Facts
- Attributes
For example, “Show me profit‑related analytics in this workspace.” lists matching objects as clickable links:
Attribute Filtering in AI Assistant
The AI Assistant can apply filters from natural language, even when you do not type exact attribute names or values. It finds the best matching value in your data and applies it automatically. This makes asking questions easier and more reliable for everyday use.
The AI Assistant understands these questions by matching values in your data. No data is shared with any LLM to enable this behavior.
How It Works:
When your question includes a value that looks like a filter, the AI Assistant searches available attributes and their values, finds the best match, and applies it to the answer or visualization.
You do not need to know the exact attribute name or value.
Examples:
You provide an attribute name and an approximate value
If you ask:
What are the total sales for product category computers?The AI Assistant:
- identifies the attribute
Product Categoryand valueComputers - searches for the closest matching value
- applies the filter, for example:
Product Category = Computers and Accessories
- identifies the attribute
You provide only a value, without naming the attribute
If you ask:
What are the total sales for computers?The AI Assistant:
- treats
computersas a filter value - finds the attribute that best matches it
- applies the filter, for example:
Product Category = Computers and Accessories
Another example:
What is my revenue coming from California?
is interpreted as:State = California- treats
No matching value is found
If you ask:
What are the total sales for kitchen appliances?And no matching value exists in your data, the AI Assistant responds with a message such as:
I couldn’t find a matching value for kitchen appliances. Try refining your question or check your data.